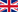
The LED (= light-emitting diode) is a diode which is able to emit light. The color of the emitted light is influenced by the material used. When a voltage is applied between the two layers (there is a negatively doped layer (n) and a positively doped layer(p)) in the direction of the flux, the excess electrons migrate towards the p-layer. Recombination then occurs in the junction layer, resulting in flashes of light (photons).
If high amounts of energy are applied, blue light is produced. If, on the other hand, only a small amount of energy is used, the light becomes red. In order to obtain warm, neutral or cold white light during illumination, the thickness of the phosphor layer must be changed accordingly. The thicker [thinner] this layer is chosen, the more yellowish [bluish] the light becomes.
The human eye is not able to detect the entire light spectrum. The visible part of the light lies between 380nm and 780nm.